In the quest for sustainable energy solutions, biomass energy has emerged as a promising contender. With its ability to convert organic materials into heat, electricity and biofuels, biomass energy presents a renewable and environmentally friendly alternative to fossil fuels. In this blog post, we will explore the concept of biomass energy, its conversion processes, environmental benefits, and the challenges and opportunities it brings.
How Biomass Energy Works?
Through a number of procedures, including direct combustion, co-firing, re-powering, combined heat and power (CHP), gasification, and anaerobic digestion, biomass is transformed into effective “biopower.”
The most straightforward and apparent way to get energy from biomass is by direct burning, which our ancestors have been doing since the beginning of time in the form of wood fires. However, some approaches are more effective and less prone to contaminate the air. Co firing at coal-fired power plants combines biomass with coal, which might provide a temporary source of somewhat cleaner energy while infrastructure for completely renewable energy is in place. “Re-powering” refers to the process of converting coal facilities to run exclusively on biomass.
The technique is known as “combined heat and power” when direct combustion is utilised to heat a building and generate energy. In order to create “syngas,” a mixture of hydrogen and carbon monoxide, biomass must be heated under pressure and exposed to a very small, carefully regulated amount of oxygen. Syngas can then be burned and passed through a gas turbine or a steam turbine to produce electricity.
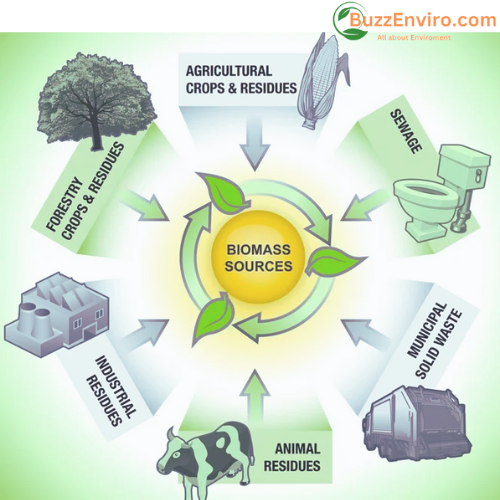
Last but not least, anaerobic digestion uses microorganisms to break down biomass in a controlled setting and release methane and carbon dioxide as greenhouse gases. This biomass production technique utilizes the generated methane for heat and electricity and prevents it from escaping to the atmosphere. It is used to handle sewage, animal manure, and landfill debris.
Pros and Cons of Biomass
Biomass energy offers various advantages and disadvantages. Let’s explore the few pros and cons of Biomass energy:
Pros of Biomass Energy
- Renewable and Abundant :- Biomass comes from organic materials known as agricultural residues, energy crops, and organic waste which can be continuously replenished. As long as sustainable practices are followed, biomass can give a constant and reliable source of energy.
- Carbon Neutrality:- Biomass energy is considered carbon-neutral because the carbon dioxide emitted during biomass combustion is offset by the carbon dioxide absorbed by plants during their growth. This helps in reducing greenhouse gas emissions and mitigating climate change.
- Waste Management:- Biomass energy offers an opportunity to divert organic waste materials, such as food waste and agricultural residues, from landfills. By utilising these waste materials for energy production, biomass energy contributes to effective waste management practices.
- Local Energy Production:- Biomass resources are often available locally, reducing the dependence on imported fossil fuels. This enhances energy security and promotes local economic development by creating jobs and supporting rural communities.’
- Diverse Application:- Biomass energy can be converted into various forms, including heat, electricity, and biofuels, making it versatile and applicable in different sectors such as heating, power generation, and transportation.
Cons of Biomass Energy
- Land Use:- Biomass production may compete with food crops for agricultural land, leading to concerns about food security and potential deforestation. Careful land management and sustainable practices are necessary to ensure biomass production does not come at the expense of food production or natural habitats.\
- Emissions and Air Quality:- While biomass energy is considered carbon-neutral, some combustion processes, especially in older or inefficient systems, can release pollutants such as particulate matter, nitrogen oxides, and volatile organic compounds. Proper emissions control and efficient combustion technologies are required to minimise air pollution.
- Energy Efficient:- Biomass energy conversion processes can be less efficient compared to fossil fuel-based systems. It often requires advanced technologies and careful optimization to achieve optimal energy efficiency and maximise energy output.
- Transportation and Storage: Biomass resources are typically bulkier and have lower energy density compared to fossil fuels. This can pose challenges in transportation, storage, and logistics, especially for long-distance transport and large-scale energy production.
- Water Consumption:- Some biomass conversion processes, such as biofuel production, may require significant water resources. Depending on the location and water availability, this could have implications for water usage and potential conflicts with other water-dependent sectors.
Conclusion
Biomass energy is a renewable and carbon-neutral alternative to fossil fuels that contributes to sustainable energy production and waste management. It has several advantages, including its renewable nature and carbon neutrality.
