In recent years, the world has witnessed a growing interest in sustainable technologies that reduce our carbon footprint while maintaining comfort in our homes. Among these innovative solutions, heat pumps have emerged as an energy-efficient alternative for both heating and cooling. By harnessing the principles of thermodynamics, heat pumps offer an environmentally friendly way to regulate indoor temperatures, making them a compelling choice for eco-conscious individuals. In this blog post, we will delve into the concept of heat pumps, their operation, benefits, and potential applications.
What are Heat Pumps?
In essence, a heat pump system is a device that transfers thermal energy from one location to another. Unlike traditional heating systems that generate heat, a heat pump works by moving heat from a colder area to a warmer one, using a small amount of energy to do so. It operates on the principle that heat naturally flows from areas with higher temperatures to areas with lower temperatures. By reversing this process, heat pumps can extract heat from the air, ground, or water and deliver it to the desired space for heating purposes.
Types of Heat Pumps
Heat pumps come in several different types, each with its own characteristics and applications. Here are some common types of heat pumps are given below:
Heat pumps come in several different types, each with its own characteristics and applications. Here are some common types of heat pumps are given below:
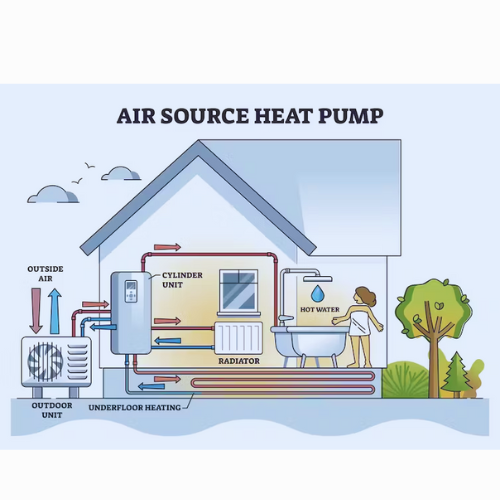
- Air-source Heat Pumps:- This is the most common type of heat pump and extracts heat from the outdoor air to heat indoor spaces during the winter. It can also reverse its operation to cool indoor spaces during the summer. Air-source heat pumps are efficient and cost-effective in moderate climates.
- Geothermal Heat Pumps:- This type of heat pump uses the stable temperature of the ground or a water source, such as a pond or well, to extract heat in the winter and provide cooling in the summer. Ground-source heat pumps are highly efficient but can be more expensive to install due to the need for underground loops.
- Water-Source Heat Pumps:- Similar to ground-source heat pumps, water-source heat pumps use a water source like a lake, river, or well to extract or dissipate heat. These systems are commonly used in commercial buildings near a large body of water.
- Absorption Heat Pump:- Absorption heat pumps use a heat source such as natural gas, propane, or solar energy to generate heat. They are often used in industrial applications and large-scale systems.
- Mini Split Heat Pumps:- Mini-split heat pumps, also known as ductless heat pumps, consist of an outdoor unit and one or more indoor units. They are used to heat or cool individual rooms or zones in a building without the need for ductwork. Mini-split heat pumps are popular for retrofitting older homes or adding HVAC systems to specific areas.
How do Heat Pumps Work?
To understand the inner workings of a heat pump, we need to familiarise ourselves with its main components: the evaporator, compressor, condenser, and expansion valve. These components work together in a continuous cycle to provide both heating and cooling.
- Evaporate:- The process begins in the evaporator, where a refrigerant absorbs heat from its surroundings (air, ground, or water). As the refrigerant evaporates, it transforms from a low-pressure liquid into a low-pressure vapour.
- Compressor:- The vaporised refrigerant is then compressed by the compressor, which increases its temperature and pressure. This step requires a small amount of energy.
- Condenser: Next, the hot, high-pressure vapor enters the condenser, where it releases its heat to the indoor environment. This heat transfer causes the refrigerant to condense back into a liquid state.
- Expansion Valve: The condensed refrigerant passes through an expansion valve, which reduces its pressure and temperature, preparing it for the next cycle.
Benefits
- Energy Efficiency: Heat pumps are known for their exceptional energy efficiency. They can produce up to three times more heat energy than the electrical energy they consume. This efficiency results in significant energy savings and lower utility bills.
- Versatility: Heat pumps are incredibly versatile as they can provide both heating and cooling. They can reverse their operation, allowing them to extract heat from indoor spaces and release it outside during warmer months, effectively acting as an air conditioner.
- Renewable Energy Integration: Heat pumps can integrate seamlessly with renewable energy sources like solar panels. The overall environmental impact can be further reduced by utilizing clean energy to power the heat pump.
- Reduced Carbon Footprint:-Heat pumps contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions by minimizing the reliance on fossil fuels for heating and cooling. They can play a vital role in mitigating climate change and achieving sustainability goals.
Application of Heat Pumps
- Residential Heating and Cooling:- Heat pumps are suitable for residential applications, providing efficient home heating and cooling solutions. They can be installed in various settings, including single-family houses, apartments, and condominiums.
- Commercial Buildings: Heat pumps are widely used in commercial buildings, such as offices, retail stores, and hotels. They offer a cost-effective and environmentally friendly option for maintaining comfortable indoor environments.
- Industrial Processes: Heat pumps can be employed in various industrial processes, such as food processing, chemical manufacturing, and pharmaceutical production. They can efficiently extract and transfer heat, contributing to energy savings and process optimization.
Conclusion
In conclusion heat pumps are an innovative and efficient solution for heating and cooling needs. By utilizing the principle of heat transfer, these devices can extract warmth from the air, ground, or water sources, providing both heating and cooling capabilities. Heat pumps offer numerous advantages, including energy savings, reduced carbon emissions, and year-round comfort. They play a crucial role in promoting sustainability and creating a greener future. As technology continues to advance, heat pumps are becoming increasingly efficient and accessible. Whether in residential or commercial settings, heat pumps are a valuable tool for creating comfortable environments while minimizing our environmental impact.
